
Identify: Is the same style applied to both headings and paragraphs if so the style needs correcting as above. Check previous paragraphs if some are correct use format painter to copy the correct style to another.Įrror 2: TOC is displaying all paragraphs of text This sometimes happens when following on from previous paragraphs if styles have not been set correctly.įix 1: Select the paragraph and apply the appropriate style that is not set to be selected for TOC. Identify: Go to the paragraph/s which are displaying in the TOC. TOC Displaying too MuchĮrror 1: TOC is displaying whole paragraphs of text Identify: This could be related to not having a style applied (see above) or the TOC is not set to pick up the correct styles you have applied.įix 2: Select the Table of Contents and then click on References Tab and select Table of Contents/Custom Table of Contents check custom settings. level 1 is displayed but not a subheading.
Table wont insert into word update#
If still not showing check to see if a style is applied to the heading you are trying to include.įix 1: If not apply the appropriate style and Update again.Įrror 2: TOC does not display all Heading levels i.e. Common Errors TOC not displaying all HeadingsĮrror 1: TOC does not contain the heading you just added to your document.
Table wont insert into word how to#
Here are some of the common errors and how to fix them. Table alignment is different from cell alignment.Tables of Contents are highly useful tools within large documents but there are several common errors that can occur when either initially producing the table or on updating the document with further information. If, however, your text isn’t the same size i.e., some cells have loads of text while others have just a bit, the alignment will make the table easier to read. If all the text is the same size, then your cells will look okay and you won’t be bothered too much about the look of the table. These settings may seem excessive however a cell is basically divided into nine sections and the alignment maps to those sections. The third row lets you align text to the left, and to the bottom of the cell, center text from the right and to the bottom of the cell, and finally, align text to the left and to the bottom of the cell. The second row lets you align text to the right but center it from the top, center the text from the right and the top, align text to the left and center it from the top. From left to right, and top to bottom, the buttons let you align text to the right, and top, center and top, and left and top. The Alignment toolbox has nine buttons for aligning text in a table in Microsoft Word. Go to the Layout tab and you will find there’s an Alignment toolbox there. This will activate the two tabs that allow you to customize the table. To change it, click inside the cell that you want to change the text alignment for. By default, the text is aligned left, and to the top of the cell. With table cells, there are two alignments to consider the left/right/center alignment that is measured in terms of the left and right border of the cell, and the top/center/bottom alignment that is measured in terms of the top and bottom border of the cell.
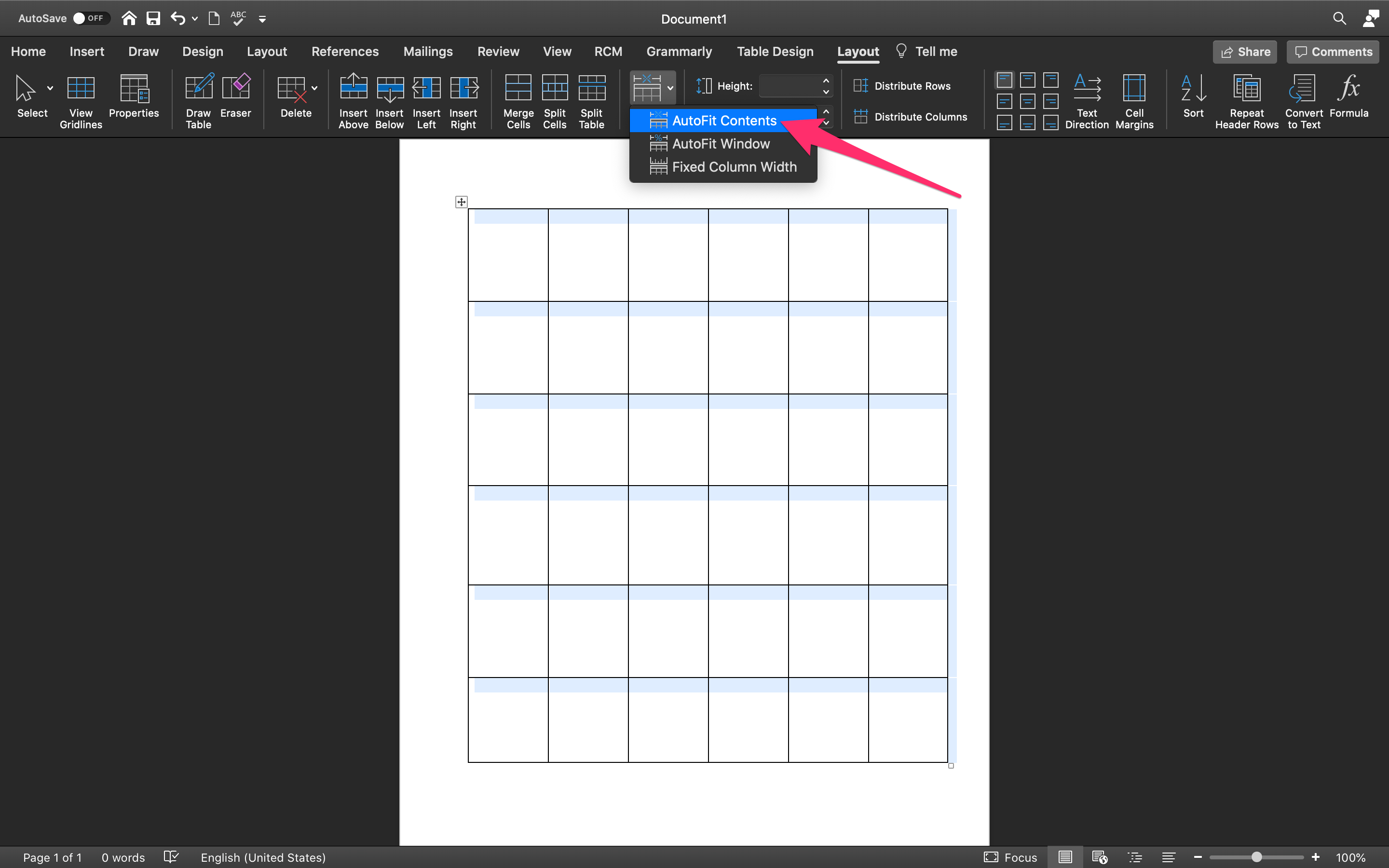
The exception being that you’re typing in a language that writes from right to left in which case the text will always be aligned to the right. When you create a table, and enter text in its various cells, it is always aligned to the left. There are dedicated buttons for it as well but they’re somewhat confusing. Where text alignment is incredibly easy to mange, it isn’t as easy to align text inside tables. The text alignment can vary for each paragraph. It’s great for when you need to meet certain academic requirements, make a stylish document, or type in different languages. The Home tab on the ribbon has dedicated buttons that allow you to left align, right align, center align, or justify text. Aligning text in Microsoft Word is incredibly simple.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
